Introduction
For some individuals, the exposure to stress can be constant. This continuous exposure can cause tension, mentally and emotionally, triggering chronic stress.
Most of the time, such individuals think of triggering events as potential threats to their coping skills, making them feel overwhelmed and unable to manage the situation. At times, this response can make them shut down multiple body systems, affecting them physically and mentally. It impacts an individual’s mood, ability to understand, immunity, and heart health. Stress management techniques work wonders for this stress to promote overall well-being.
“The greatest weapon against stress is our ability to choose one thought over another.” -William James [1]
Understanding Chronic Stress
At the end of a hectic day, when we ask our friends and family how their day went, we would most likely get the answer: “It was stressful.” Stress is a normal part of our life. Some level of stress is needed to perform daily activities and accomplish tasks at work.
However, when the stress levels start moving toward overload and burnout frequently, a person can be said to have Chronic Stress. Chronic stress can drastically affect a person’s physical and mental health [2].
Such individuals become more susceptible to anxiety disorders and depression. They may find it challenging to manage their emotions and have memory issues. Therefore, it can impact not only brain function but its structure as well [4].
Stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are released when we face stress. It forces the overproduction of these hormones, harming the cardiovascular system and leading to hypertension, high cholesterol, and higher chances of heart disease [4].
All these issues can weaken the immune system, which means that an individual can catch infections and diseases more frequently.
Causes of Chronic Stress
Our modern-day lives are fast-paced, which means that chronic stress responses can get triggered. [3]:
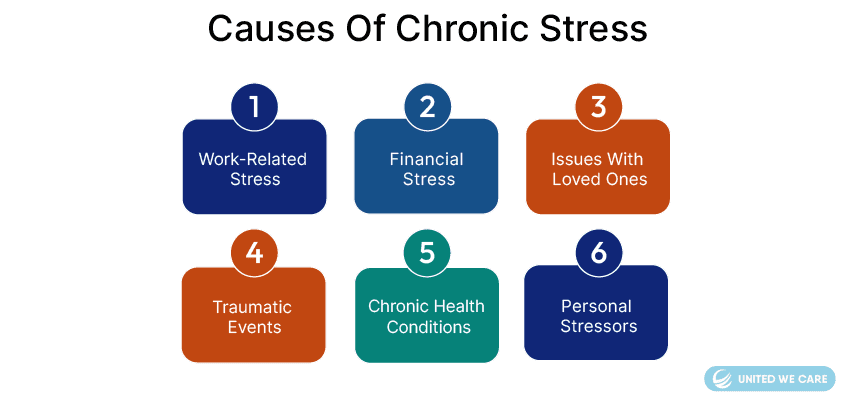
- Work-Related Stress: Corporate lives involve facing competition day in and day out. Working professionals may have enormous amounts of work and long work hours. Despite the hard work, they may face job insecurity and have no control over their tasks.
- Financial Stress: The higher a person’s income is, the more financial pressures they may have. They may be the only earning member to meet the family’s basic needs or have EMIs to pay. All this can lead to constant financial tension, anxiety, and increased stress levels.
- Issues With Loved Ones: Our loved ones may also be constant sources of stress: family, friends, partners, and colleagues. They may contribute to chronic stress through conflicts, lack of communication, and lack of understanding.
- Traumatic Events: 70% of the world’s population has faced at least one traumatic event in their lives, such as accidents, natural disasters, and physical or emotional abuse. Such individuals are more likely to develop chronic stress.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Everybody wants to lead a healthy life without illnesses. However, lifelong illnesses like hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, arthritis, or chronic pain need coping and management, which can lead to prolonged stress.
- Personal Stressors: Some people are perfectionists and want things in a particular way. Any change or things not going as per them can trigger chronic stress. Other factors like negative thought processes and lack of coping skills can also contribute to chronic stress.
Symptoms of Chronic Stress
Stress is a normal response of the body and does not hamper our daily lives largely. Chronic stress, on the other hand, can affect the entire body physically mentally, and behaviorally [4] [5]:
- Physical Symptoms: If you suffer from constant headaches, frequent infections, irritable bowel syndrome, muscle tension, digestion issues, and chronic pain, then it is highly likely that you have chronic stress. All these symptoms happen due to elevated stress hormones.
- Emotional Symptoms: Notice how you react to people’s demands. If you easily get irritated, nervous, anxious, or even start crying, chronic stress has already set in. Chronic stress can even lead to depression.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Chronic stress can impact cognitive function drastically, causing issues like lack of concentration and focus, memory issues, and difficulty in making decisions.
- Sleep Issues: Sleep issues are directly correlated with chronic stress. Difficulty falling asleep and waking up feeling tired even after 8 hours of sleep can be symptoms of chronic stress.
- Appetite Changes: You might have seen some famous people talk about stress-eating. Such changes in appetite, whether it is overeating or loss of appetite, are indicators of chronic stress. These changes in appetite become more visible with weight fluctuations. Your immunity might also get compromised.
- Withdrawal from Social Interactions: Chronic stress can set low self-esteem and self-confidence. Due to this, individuals may want to avoid socializing with their near and dear ones. Chronic stress can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Read more about – Does Stress Cause Cancer
Overcoming Chronic Stress
Even though you might have lived with high stress levels for a long time, it is possible to manage and reduce chronic stress [5] [6]:
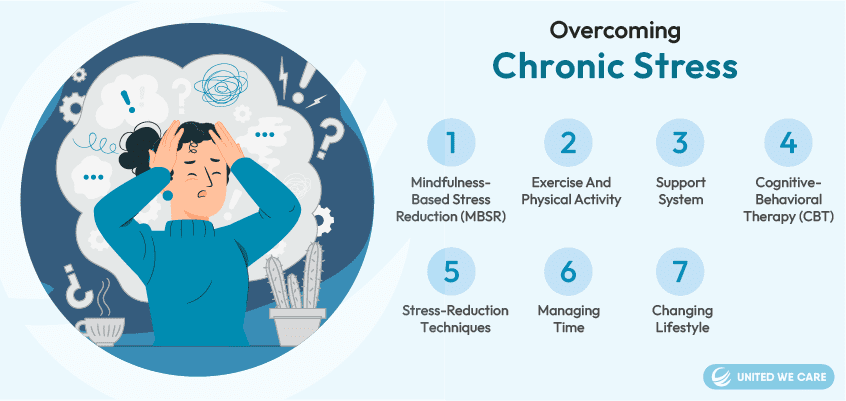
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): MBSR Therapy utilizes meditation, yoga, and mindfulness techniques. Combining these techniques helps reduce stress and improve mental, emotional, physical, and behavioral well-being.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Indulging in physical activity, such as walking, running, and dancing, can produce happy hormones like endorphins and dopamine. These hormones help elevate chronic stress.
- Support System: Talking to loved ones, be it friends, family, or people in a support group, can significantly reduce stress. Feel free to ask your support system to lend you a listening ear and provide advice.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT works on the identification of negative thought patterns and behavioral problems. Doing so can help break the patterns that can add to chronic stress and cause harm to the body.
- Stress-Reduction Techniques: Stress can be reduced relatively by using deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery. These techniques work as a distraction from the stressor.
- Managing Time: An individual dealing with chronic stress must learn to manage time. Set reminders, plan your day well, and prioritize tasks to find a balance between professional and personal lives.
- Changing Lifestyle: Allow yourself to adopt a healthy lifestyle by incorporating healthy food habits, getting sufficient sleep, avoiding alcohol and drugs, and minimizing caffeine intake can improve stress response drastically.
Read more about Chronic disease and mental health
Conclusion
Stress is fundamentally important for all individuals. However, prolonged exposure to stressors can lead to chronic stress. Chronic stress can harm an individual physically, mentally, emotionally, and behaviorally. It can lead to anxiety, depression, a weakened immune system, heart disease, hypertension, and other adverse conditions. Even if these adverse conditions are seemingly irreversible, you can effectively manage them by using mindfulness, relaxation, changing your lifestyle, participating in physical activity, and seeking professional help.
If you’re dealing with chronic stress, don’t hesitate to seek support from our expert counselors or explore valuable content at United We Care! Our team of wellness and mental health experts is here to provide guidance and the best methods for improving your well-being.
References
[1] “Calmness in Chaos,” Calmness in Chaos – Energy Yoga and Wellness. https://energyyoga.com/quotes/calmness-in-chaos
[2] “How Chronic Stress Impacts Your Health,” Verywell Mind, May 17, 2023. https://www.verywellmind.com/chronic-stress-3145104
[3] “Causes of Stress,” WebMD, Mar. 16, 2022. https://www.webmd.com/balance/causes-of-stress
[4] “Mind and Health,” The Human Journey. https://humanjourney.us/health-and-education-in-the-modern-world-section/mind-and-health/
[5] “Blog | 6 ways to reduce chronic stress,” Reid Health. https://www.reidhealth.org/blog/6-ways-to-reduce-chronic-stress
[6] “A Simple Way to Combat Chronic Stress,” Harvard Business Review, Apr. 15, 2016. https://hbr.org/2016/04/steps-to-take-if-youre-suffering-from-chronic-stress