Introduction
Dealing with someone who experiences delusional thoughts is similar to someone who has hallucinations. However, more non-verbal treatment techniques are used in the case of delusional disorders. Therefore staying silent longer and having more patience with the individual is essential as even though they may not voice their delusions, they are always with them. To better understand how to deal with this disorder, therefore it is best first to understand delusion and why some people suffer from delusionary disorders.
Our Wellness Programs
What is delusion?
Definition of delusion[1] is an individual’s fixed, false belief that usually conflicts with reality. Hence a person in a delusional state may not be able to let go of their convictions and opinions even when there is contrary evidence shown to them. People may even reinforce their false beliefs because they have misinterpreted a situation.
Not all delusions are the same; as well as there are times when an individual may believe what is possible in real life. Hence other times, the delusion could be bizarre, impossible, and unbelievable without having any real roots.
However, delusions can also be a symptom of a deeper mental health issue, such as psychotic disorders. They can also occur as hallucinations, the perception of something not really there.
Looking for services related to this subject? Get in touch with these experts today!!
Experts

Mansi Chawla

India
Psychologist
Experience: 12 years

Esha M. Puneyani

India
Psychologist
Experience: 14 years

Banani Das Dhar

India
Wellness Expert
Experience: 7 years

Anuj Khandelwal

India
Psychiatrist
Experience: 10 years
Rishab Verma

India
Psychiatrist
Experience: 1 years
What is delusional disorder?
Delusional disorder, previously known as paranoid disorder, so that it is a severe mental illness characterised by the inability of an individual to tell what is real from imagination. Hence delusion is one of the main symptoms of delusional disorder. Definition of a person is to suffer from such an illness when the doctors have entirely ruled out any physical reason for the delusions.
People who experience delusional disorder can often continue to function normally in society despite their delusion. They do not usually behave oddly, unlike those who experience other psychotic disorders. However, there are times when an individual can get so caught up in their delusion that it may disrupt their lives, making them unequipped to handle day-to-day lives.
The most common occurrence of delusional disorder is in middle-to-late life; it is often more common in women than in males.
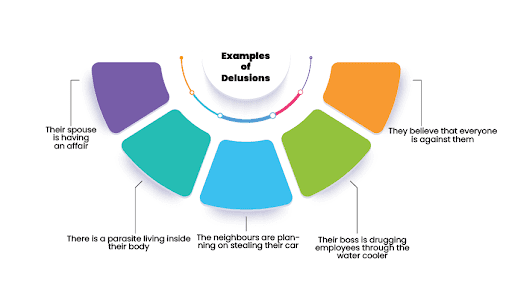
Which of the following is an example of delusional disorder?
There are several examples of delusional disorders, from believing that their co-workers are conspiring against them to being convinced that someone on television is in love with them. A person with such delusions will genuinely think this is a fact, and they may use vague terms and seem suspicious or agitated most of the time.
A person can be diagnosed with a delusional disorder if they experience one or more delusions for over a month.
Examples of delusions
- The neighbours are planning on stealing their car.
- Their spouse is having an affair.
- They have the power to save the entire universe, and they have to complete a set of tasks every day to keep the earth functioning as it is.
- There is a parasite living inside their body.
- Someone famous is sending them secret hand signals through the television.
- Their boss is drugging employees through the water cooler.
- They believe that everyone is against them.
How many types of delusions are there?
There are several different types of delusion, categorised on the belief of the person suffering from the delusion.
- Persecutory delusion,[2]
- Delusional jealousy,
- Erotomania/delusion of love,
- Delusion of grandeur,
- Somatic delusional disorder,
- Induced delusional disorder/folie a’ Deux,
- Mixed delusion
1. Persecutory delusion
Persecutory delusion[3] is one of the most common types of delusion. In this type, the person believes they are being spied upon, stalked, harassed, conspired against, poisoned, or obstructed by other individuals or organisations.
2. Delusional jealousy
In this case, the person strongly believes their partner or spouse is cheating on them, and they may go to great lengths to prove their suspicions. Some individuals suffering from this delusion may hire a private investigator to follow their partner.
3. Erotomania/delusion of love
Here, the individual suffering from the delusion has an obsession with someone and believes that this person is also in love. It could lead to him/her stalking the object of his/her affection and displaying unnatural jealousy or rage when the suffering person sees his/her loved one with their spouse. A celebrity or someone famous is usually the object of erotomania.
4. Delusion of grandeur
In this kind of delusion, a person may believe they are more significant or influential than they are. Usually, they imagine they have extravagant wealth, exceptional talent, or are in a special relationship with someone prominent.
5. Somatic delusional disorder
The person suffering from such disorders believes that something is wrong with them. They may often consult multiple specialists and physicians and even go as far as plastic surgery to rectify the problem.
6. Induced delusional disorder/folie a’ Deux
It is a rare form of delusion in which two people who are usually in a close relationship believe the same delusion.
7. Mixed delusion
If an individual suffers from two or more of the delusions mentioned above, they are said to have a mixed delusion.
What is the treatment of delusion?
The treatment usually includes the use of both medication and psychotherapy. However, it depends on the severity of the delusion. Hospitalisation may be necessary and avoid the patient’s risk of hurting themselves or others.
1. Psychosocial treatments
In this sort of therapy, individuals should teach how to control their symptoms and identify the early signs of relapse to avoid them in the future. Individual psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioural therapy, and family therapy are usually the three types of treatments tried.
2. Medicines
Anti-psychotics are the primary medication used to treat severe delusional disorders. Most medication prescribed to a person with delusion works by blocking dopamines and some serotonin receptors in the brain to avoid delusions. There Antidepressants and tranquillisers may also be used in some cases.
While there is no known way in which a person can prevent delusional disorders talking to a mental health professional can help them cope with the condition and live everyday lives. United We Care has a range of expertise that focuses on bettering an individual’s mental health both in India and Canada.
| [1] | M. Spitzer, “On defining delusions,” Compr. Psychiatry, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 377–397, 1990. |
| [2] | R. P. Bentall, R. Corcoran, R. Howard, N. Blackwood, and P. Kinderman, “Persecutory delusions:,” Clin. Psychol. Rev., vol. 21, no. 8, pp. 1143–1192, 2001. |
| [3] | D. Freeman, P. A. Garety, E. Kuipers, D. Fowler, and P. E. Bebbington, “A cognitive model of persecutory delusions,” Br. J. Clin. Psychol., vol. 41, no. Pt 4, pp. 331–347, 2002. |