Introduction
Elderly individuals experience memory loss and face difficulty or cannot carry out daily activities. It is a normal physiological process due to age-related degeneration known as dementia. Most people are unaware until it becomes severe enough to affect their everyday lives. Let us discuss more in-depth and get to know some essential facts related to dementia.
Our Wellness Programs
What is Dementia?
Dementia is a group of neurological disorders affecting the brain and its functioning. It is not a disease, but other conditions can cause dementia-like symptoms. Dementia occurs and progresses in stages, ranging from the no impairment stage to the severely impaired location.
- Symptom-less stage: No visible symptoms exist, but random testing may show brain involvement.
- Very mild symptoms: The individual may show slight changes in their routine and behaviour. At this stage, a person is entirely independent.
- Mild symptoms: In this stage, memory loss is noticeable and affects daily activities. They face difficulty in planning and remembering things or events.
- Moderate symptoms: There is a gradual decline in the individual’s independence. Increasing difficulty in reasoning, planning, remembering, and managing money matters. Reaching home within a previously well-known community is a vital sign seen in this stage.
- Moderately severe symptoms: The characteristics of this stage include the failure to recognise one’s family members and their names. There is a lack of time and day orientation, for example, not knowing what day it is. Dependence on others increases significantly.
- Severe symptoms: Daily activities like toilet and eating, bathing, and wearing clothes seem a huge task, and an around-the-clock caregiver is required to be with the individual.
- Very severe symptoms: Individuals in this stage of dementia are bed-bound and can no longer carry out any activity without complete help from a caregiver.
The probable pathology behind dementia is damage occurring to the brain’s neurons (brain cells) and damage to the brain’s memory, decision-making, learning, and spoken language areas. It explains the symptoms occurring in dementia.
Looking for services related to this subject? Get in touch with these experts today!!
Experts

Neelam Parwani

India
Life Coach
Experience: 5 years

Mansi Chawla

India
Psychologist
Experience: 12 years

Sapna Zarwal

India
Psychologist
Experience: 19 years
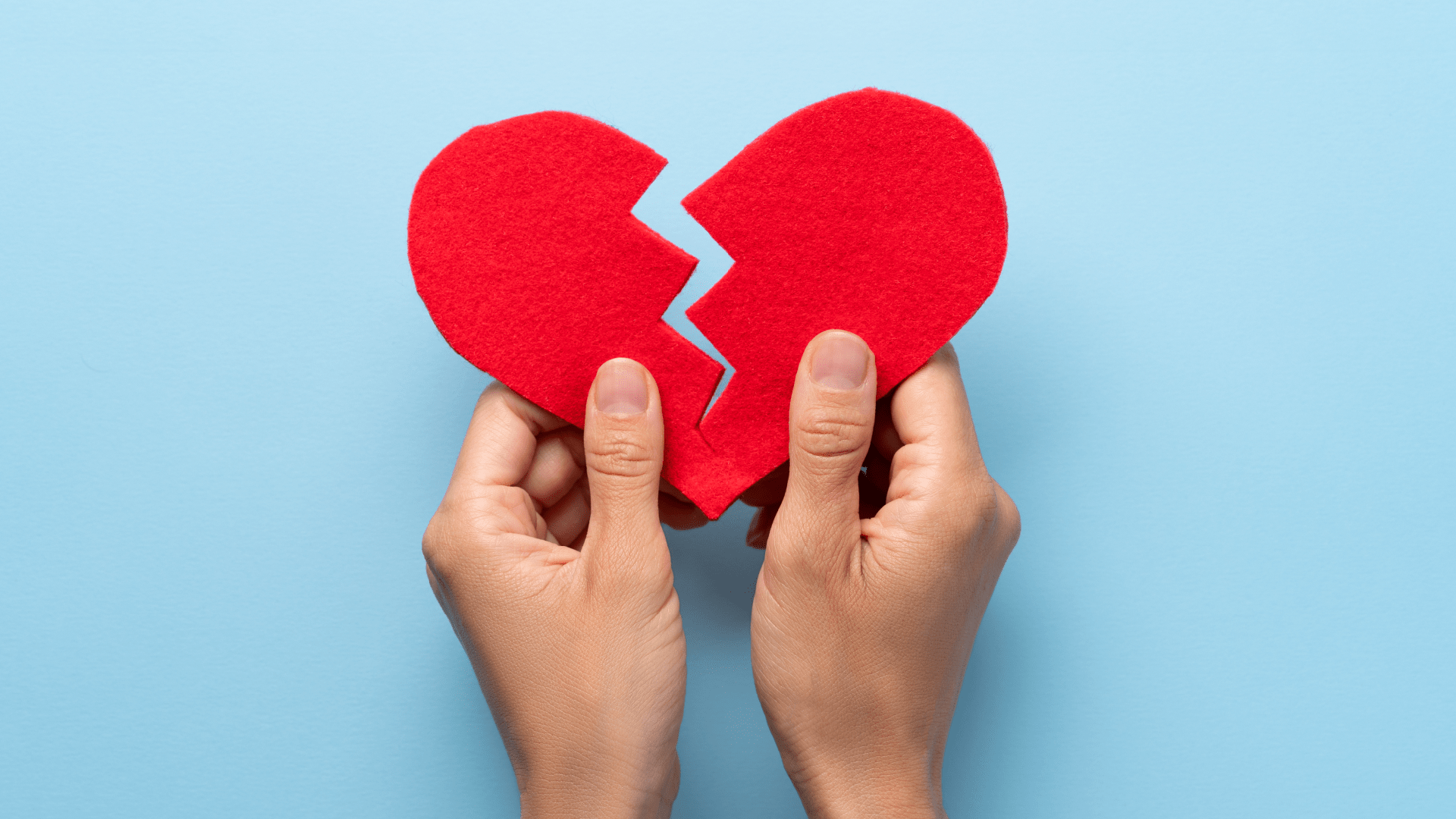
What are the symptoms of Dementia?
The most common symptoms of dementia involve loss of memory, irrelevant talk, difficulty understanding things quickly, and dependence on daily activities. Let’s talk about these in more detail.
- Loss of memory: There are some categories of memory loss – (a) short-term memory loss and (b) long-term memory loss. Inability to remember names, time, food, and recent events comprises short-term memory loss, whereas not being able to recognise the birth date, marriage anniversary, etc., is long-term memory loss. One may forget the way to their home, where they are at present, and what should they do next.
- Communication issues: Someone with dementia would find it difficult to understand words. It would also be hard for them to communicate their needs. Their speech would include repetitive questions and other problems with comprehension.
- Difficulty in daily activities: As the person cannot remember how and when they need to do certain things, there is initial difficulty in performing basic tasks. It eventually leads to a continuous dependence on caregivers.
- Changes in behaviour: The person would also experience anxiety, depression, irritation, and mood swings in increasing intensity.
What are the causes of Dementia?
Dementia is a symptom or entity seen in neurological and other ailments like:
- Parkinson’s disease: Progressive stages of Parkinson’s disease cause dementia.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s disease is known to cause plaques or depositions that damage brain neurons, causing dementia.
- Multiple sclerosis: It’s a neurodegenerative disease that eventually causes brain cells to become weak.
- Vitamin deficiency: Vitamin B12, B1, B6, E, and copper deficiencies can cause symptoms of dementia.
- Cancer: Rare cause, but some brain tumours cause dementia.
- Other causes include low blood sugar levels and hypothyroidism, Chronic alcohol consumption, and Accidents damaging the brain and skull.
How does Dementia affect your daily life?
Dementia is not just about memory loss, and it’s much more than that. Not just the individual but everyone around also is significantly affected. Family and caregivers must constantly be around the affected person to help carry out essential activities. Others need to remind them to eat, bathe, sit up, walk, empty their bowel and bladder and how to wear and change clothes, shoes, etc. In severe stages, there is complete dependence, and the individual is bed-bound for most of his life. Changes in behaviour may lead to loss of social skills and other individuals refraining from interacting with the affected person. It may cause depression and increase symptoms of dementia.
How to treat Dementia?
Research has implied that there is no known cure for dementia. It is best to prevent dementia by maintaining a routine of physical activity, a healthy diet, social interactions, and being alert to possible symptoms.
Doctors should identify dementia before treating the symptoms. A doctor will usually test for neurological and other diseases that might be causing transient symptoms of dementia. Treatment of the underlying cause of dementia will induce remission of dementia symptoms.
Conclusion
Dementia is a slowly progressive neurological disorder affecting the brain cells. It causes a loss of memory and difficulty understanding, reasoning, thinking, planning, and remembering things and events. There is increasing difficulty in day-to-day activities, eventually leading to bedridden and complete dependence on the caregiver. It occurs due to neurological ailments like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other nutritional disorders. The primary management approach is to prevent dementia and treat the underlying cause through medications.